We are excited to announce the release of the Memory Analysis 0.7 package, which is currently in beta. This version introduces significant improvements that partly stem from testing our solution against various CTF challenges.
These new features, together with the recent release of Cerbero Suite 8.6, make this update particularly noteworthy. Thanks to the sophisticated caching mechanism implemented in the latest release of Cerbero Suite, memory analysis is now faster than ever. If you thought it was already fast, you are in for a surprise!
- File Scan
- Pool Scan
- Multi-Format Input
- VMEM and VMSS Format Support
- NT/LM Password Hash Decryption
- User-Mode Memory Region Exclusion
- Unlinked Processes Detection
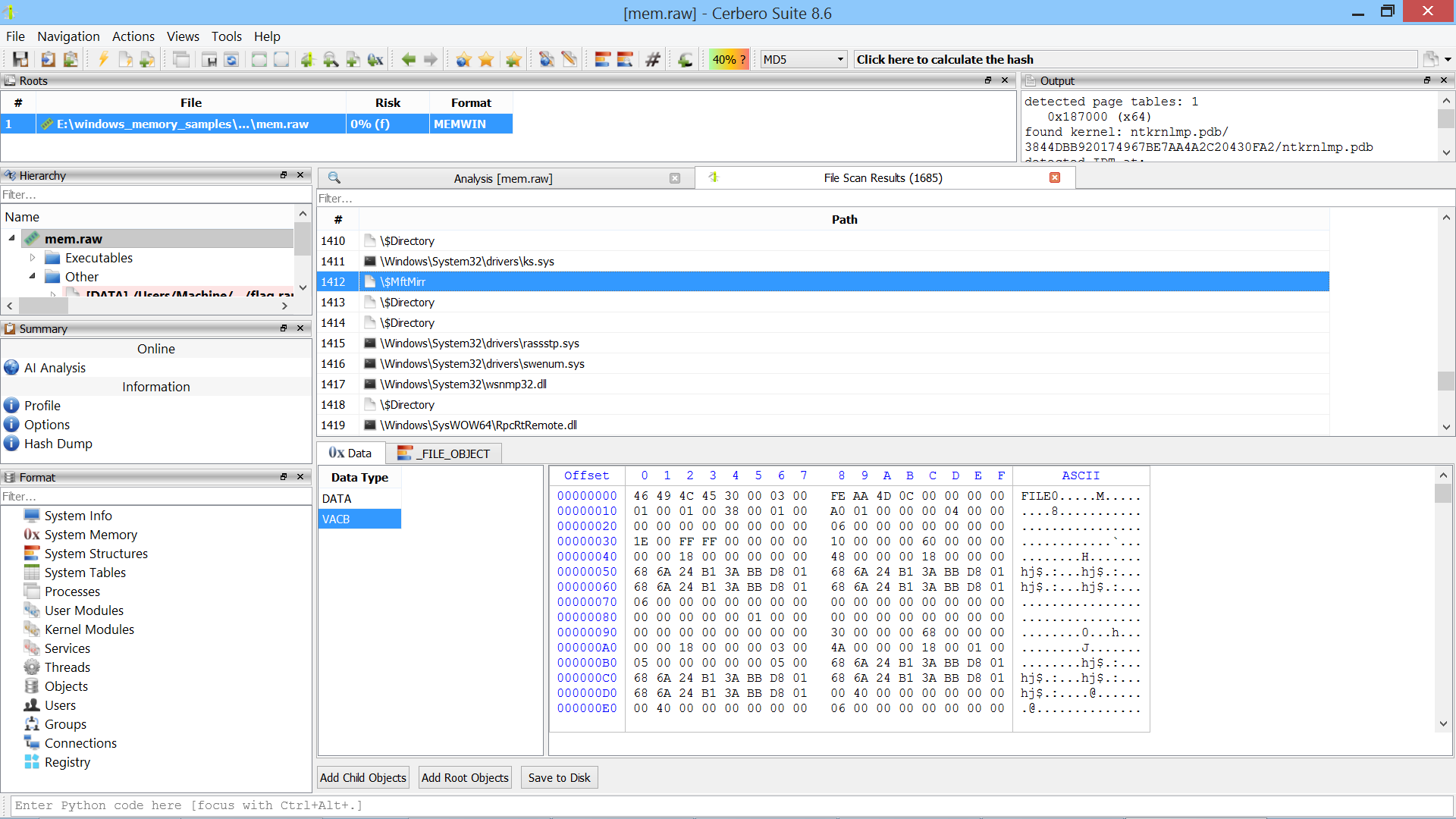
File Scan
The package now includes an action that lets you scan and extract files directly from memory.
All cache types are supported, so if a file was cached in memory, it can be extracted.
Pool Scan
You can now scan memory pools for specific items of your choice.
For each pool item found, you can inspect its associated structures and data in detail.
Multi-Format Input
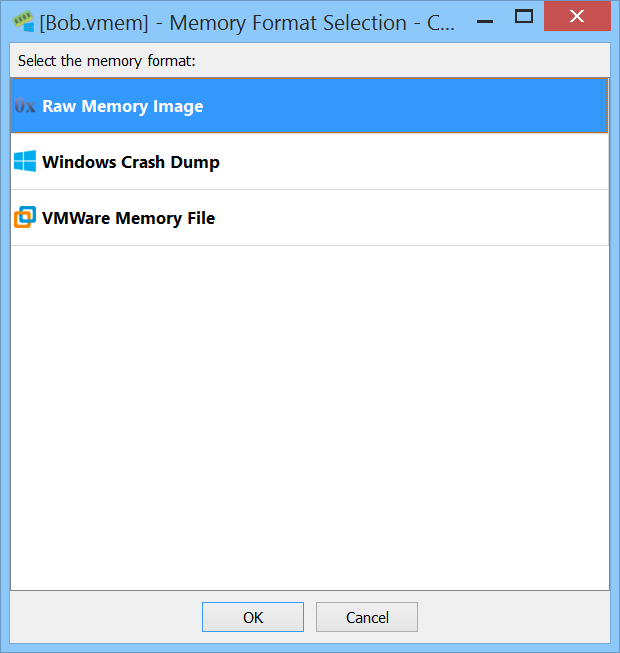
Previously, while the Windows Crash Dump format was supported through its dedicated package, analyzing its memory snapshot required opening it as a standard file. That is no longer the case.
The memory analysis logic provider now accepts multiple input formats and automatically detects the correct one. When opening a memory dump, a dialog prompts you to select the intended format.
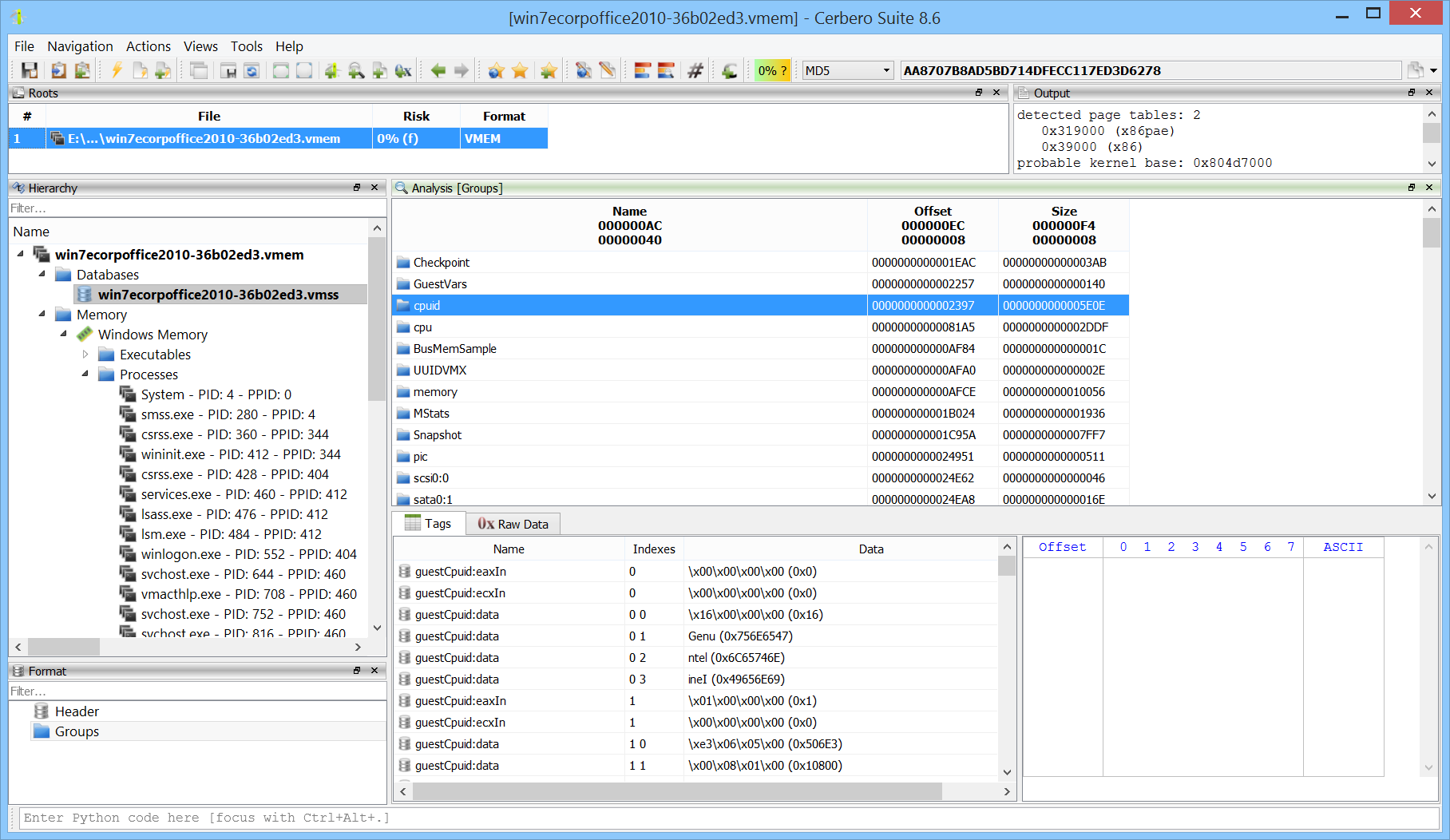
VMEM and VMSS Format Support
The VMWare VMEM format is now fully supported. Although VMEM files can sometimes represent raw memory, they sometimes rely on an accompanying VMSS (VMWare Suspended Status) file to properly reconstruct memory mappings.
Support has been added not only for the VMEM format but also for inspecting VMSS files directly, which can contain valuable state information and other useful data.
NT/LM Password Hash Decryption
NT/LM password hashes are now decrypted automatically, allowing them to be exported and cracked using tools such as hashcat or John the Ripper Jumbo.
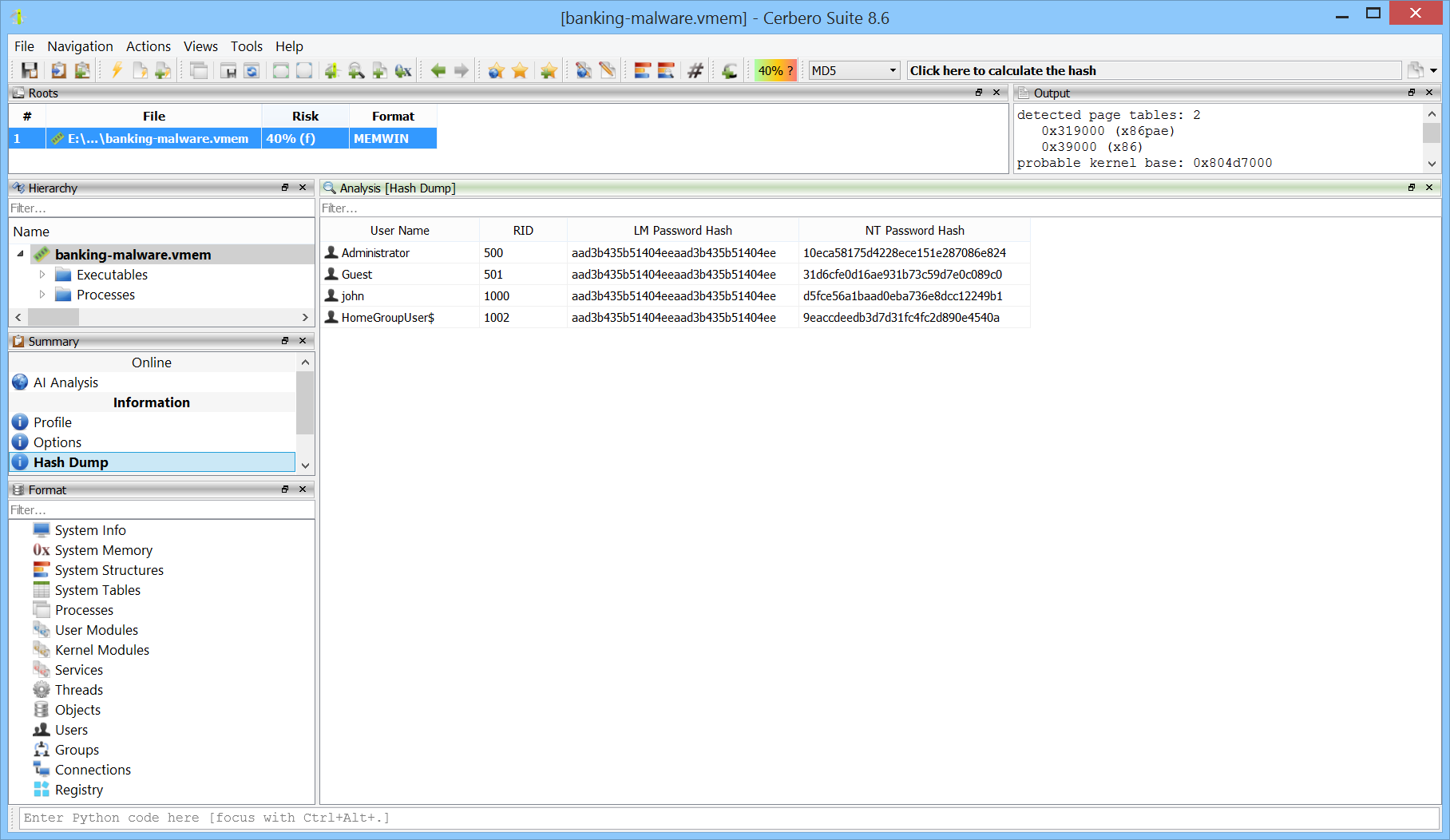
This capability is especially valuable in digital forensics, where recovered credentials can help identify attacker behavior, detect privilege escalation, or uncover unauthorized access.
User-Mode Memory Region Exclusion
There are times when it is necessary to operate only on selected user-mode memory while excluding specific regions, for instance large reserved areas that slow down analysis. In one of the CTF challenges, we had to copy part of a process’s memory to skip such a region to improve performance.
Now, you can exclude any user-mode memory region simply by unchecking it, and the exclusion is reflected immediately in the hex view. This allows for faster mining of files, string searches, and other operations.
Unlinked Processes Detection
It is now possible to detect unlinked processes directly by specifying it in the options.
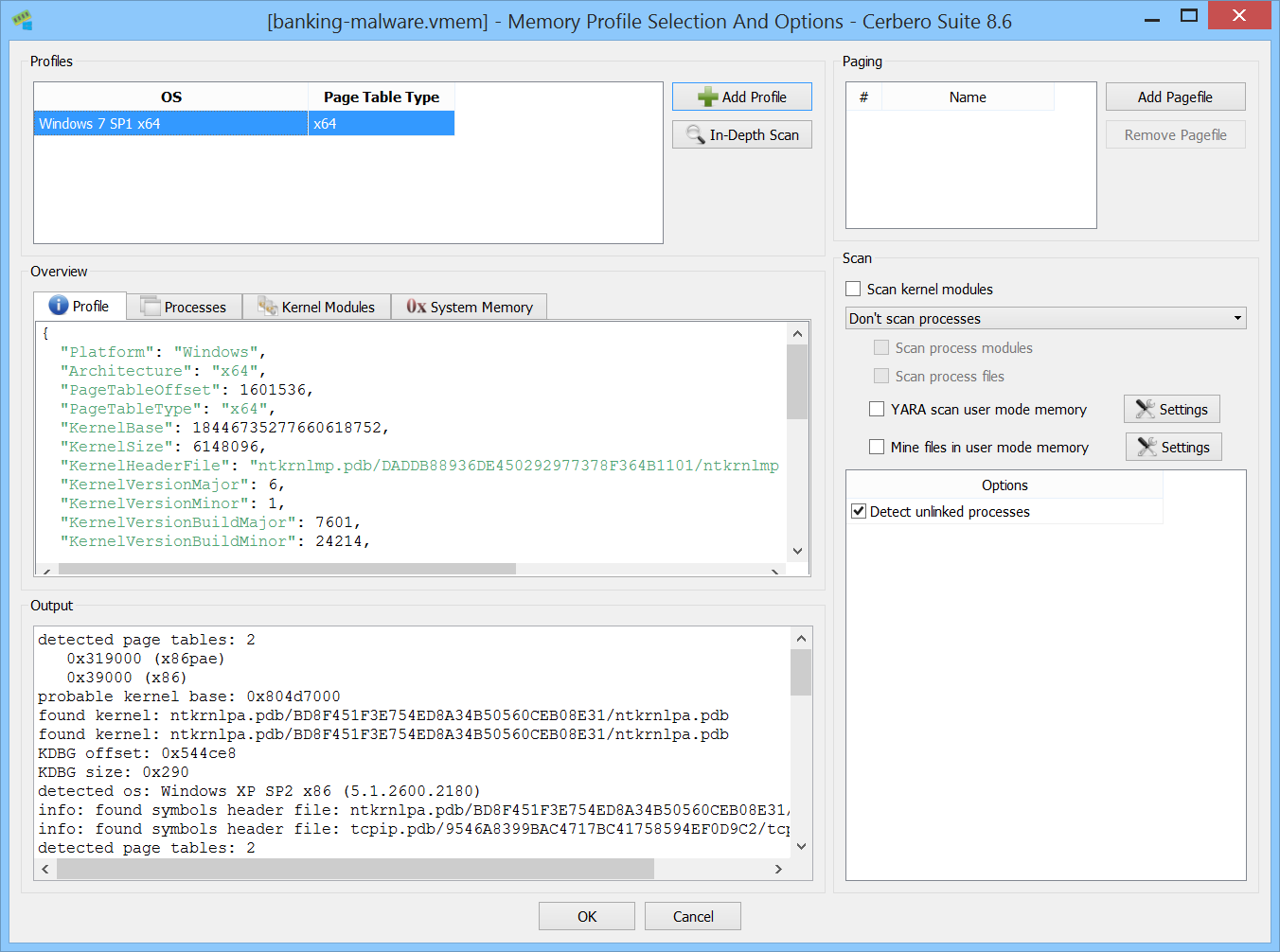
Unlinked processes may appear as artifacts of dumping a live system or as a deliberate technique used by malware to hide from process listings. In the image below, you can see a malicious process that unlinked itself from the list of active processes.
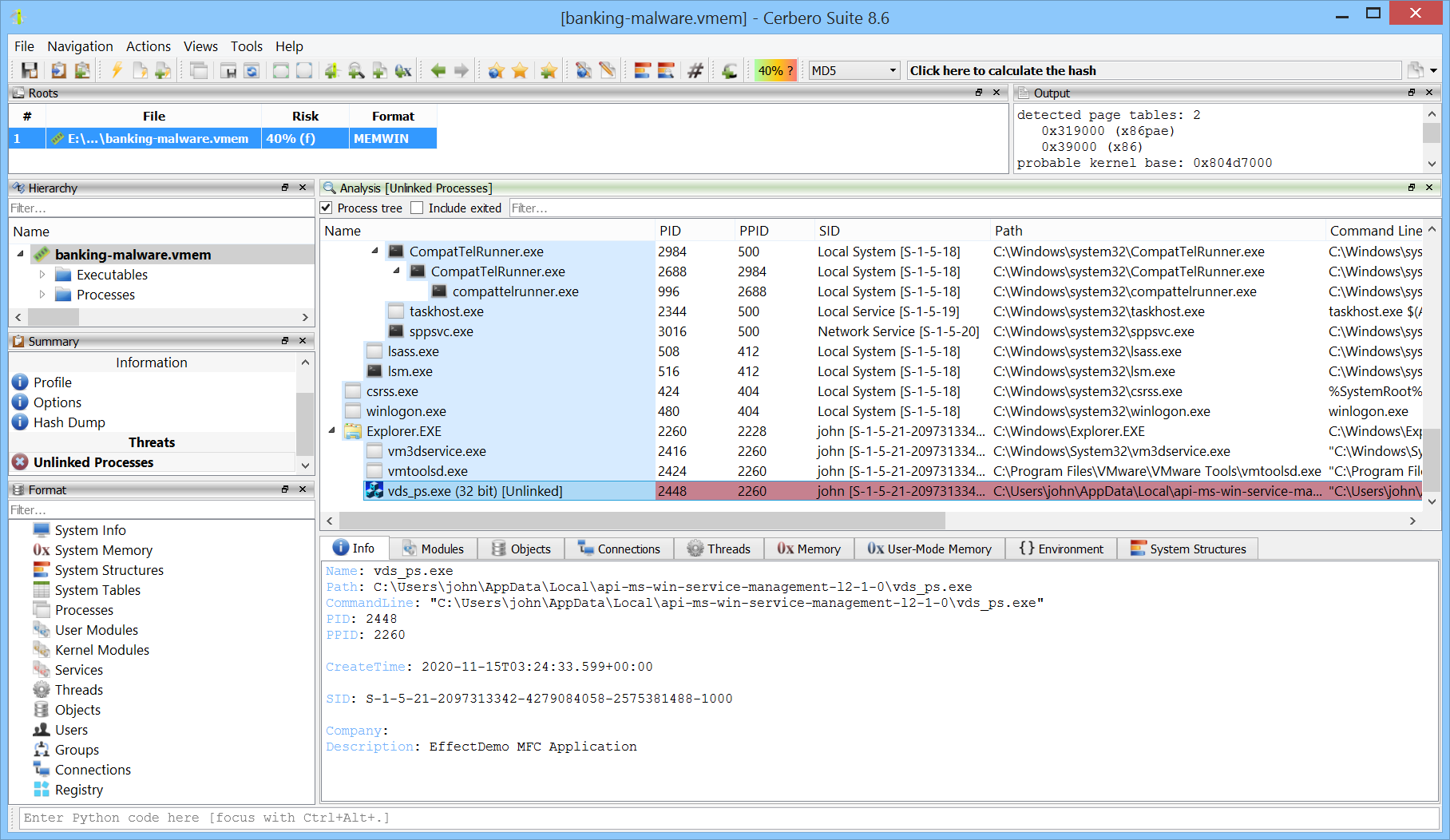
We are very enthusiastic about the progress of the Memory Analysis package and look forward to demonstrating these features in action, particularly through real-world CTF challenges.